CISSP
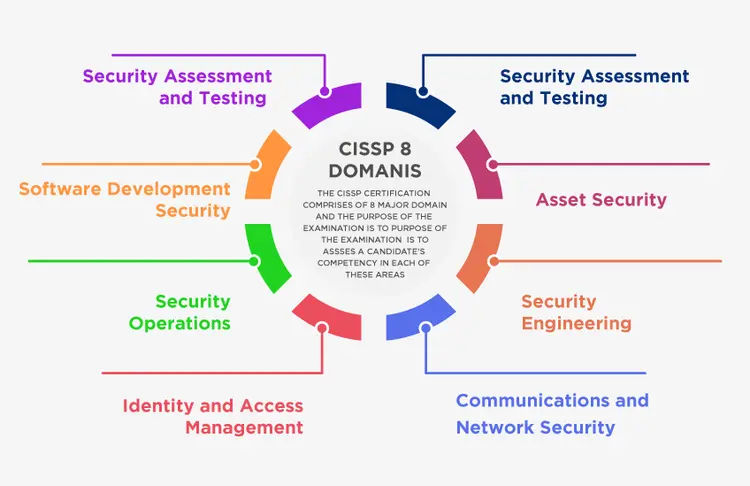
CISSP stands for Certified Information Systems Security Professional. It is a globally recognized certification for experienced cybersecurity professionals. Eight domains are covered for this exam.
Security and Risk Management
Defines security goals and objectives, risk mitigation, compliance, business continuity, and the law. Security analysts may need to update company policies regarding customers’ health data in compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Asset Security
Secures digital and physical assets. It’s also related to the storage, maintenance, retention, and destruction of data. Security analysts may be tasked with properly destroying old equipment, especially regarding confidential information.
Security Architecture and Engineering
Optimizes data security by ensuring effective tools, systems, and processes are in place. Security analysts may be tasked with configuring a firewall. A firewall is a device that monitors and filters incoming and outgoing computer network traffic, which helps prevent attacks.
Communications and Network Security
Manage and secure physical networks and wireless communications. Security analysts may be tasked to analyze user behavior within the organization. For example, connecting to an unsecured wireless hotspot, the analyst would create a network policy to prevent and mitigate exposure.
Identity and Access Management
Keeps data secure by ensuring users follow established policies to control and manage physical assets, like office spaces, and logical assets, such as networks and applications. A security analyst may need to validate the identities of employees and document access roles, or employee keycard access.
Security Assessment and Testing
Conducting security control testing, collecting and analyzing data, and conducting security audits to monitor for risks, threats, and vulnerabilities. Security analysts conduct regular audits of user permissions to make sure that users have the correct level of access, such as payroll information access is often limited to certain employees.
Security Operations
Conducting investigations and implementing preventative measures. A security analyst would need to follow the procedures outlined by the organization if an unknown device is connected to the network.
Software Development Security
Uses secure coding practices, which are a set of recommended guidelines that are used to create secure applications and services. A security analyst would work with software development teams to ensure practices are incorporated into the software development lifecycle, such as advising on. password policies and any user data are properly managed.